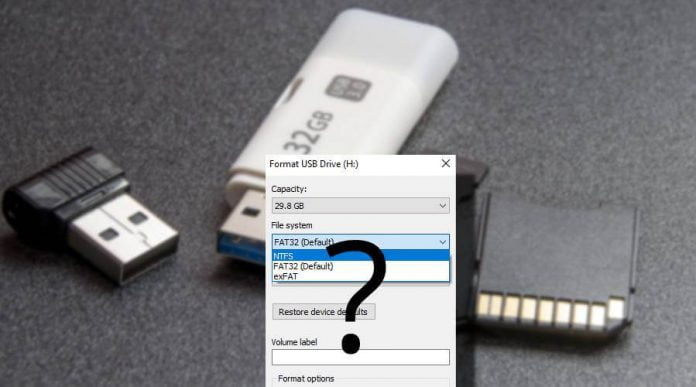
Did you notice that whenever you format a USB drive with Windows, it always gives you three different file systems options to choose from — NTFS, FAT32 and exFAT. By default, Windows chooses FAT32 file format for your USB drive, leaving us wondering — what happens if we choose other file formats?
Sadly, Windows doesn’t provide any information about these file systems, so a normal user always go with the default settings. Since this default setting works most of the time without any problem. But don’t you eager to know what happens if we choose NTFS or exFAT instead of FAT32 or why Windows automatically select FAT32 as the default one?
So in this article, we are going to break it down for you — we will explain the difference between NTFS, FAT32 and exFAT. What are their advantages and disadvantages? How will they work with each operating system? And under what circumstances we should choose any of these particular file systems? and more.
What is File System?
Before knowing the difference between NTFS, FAT32 and exFAT file formats, first, you should know — what is a file system?
The file system is a method used by operating systems to organize data on drives. The data is usually organized in folders called directories, which can contain other folders and files. File systems also specify how data is stored on the drive and what type of information can be attached to the file such as file names, permissions and other attributes.
Many operating systems include support for more than one file system. Microsoft Windows mainly makes use of the NTFS, FAT32 and exFAT file systems. So we are going to discuss these three file systems in detail here.
NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT — Which one is best?
NTFS:
NTFS (New Technology File System) is a modern file system used by Microsoft Windows and was introduced with the Windows NT operating system in 1993. Windows uses the NTFS file system as its system drive and most non-removable drives. Like, when you install Windows, it formats your system drive (C: drive) with the NTFS file system. NTFS has file size and partition size limits that are so theoretically huge enough that you won’t run up against them.
Features: NTFS is packed with modern features. It supports file permissions for security, a change journal that can help quickly recover errors if your computer crashes, shadow copies for backups, encryption, disk quota limits, hard links, and other various features. Many of these are crucial for an operating system drive — especially file permissions.
Compatibility: NTFS will work with all recent versions of Windows but it has limited compatibility with other operating systems. By default, Mac OS X can only read NTFS drives, not write to them. Some Linux distributions may enable NTFS-writing support, but some may be read-only.
Choosing NTFS file system while formatting USB drive:
Now comes to our point, when you should choose NTFS as a file system while formatting a USB drive?
Since NTFS is a fully Windows compatible file system, it will work with all Windows versions. And some special cases:
- choose if you are formatting a USB drive larger than 32GB
- choose when your file size is more than 4GB because the default option, FAT32, supports individual file sizes up to 4GB.
- choose if you are moving a portable Windows program
- choose if you are using a USB flash drive to boot the operating system
The drawback of the NTFS file system is it got a lot of extra overhead that you only requires if you’re running Windows.
Fat32:
FAT32 (File Allocation Table) is the oldest of the three file systems available to Windows. It was introduced all the way back in Windows 95 to replace the older FAT16 file system. Flash drives you purchase will often come formatted with FAT32 for maximum compatibility across not just modern computers but other devices like game consoles and anything with a USB port.
Features: It’s so old, it has great compatibility across many old and modern computers with USB support. The family of FAT file system is supported by almost all operating systems for personal computers.
Compatibility: Works with all versions of Windows, Mac, Linux, game consoles, and practically anything with a USB port.
Choosing FAT32 file system while formatting USB drive:
However, FAT32 is the default file system chosen by Windows because of its compatibility with all operating systems. And other instances are:
- choose FAT32 for less disk space wastage and more reliability.
- USB drives smaller than 32 GB that doesn’t require any security.
- if you are transferring files lesser than 4GB in size.
- to work with all operating systems.
FAT32 file system’s age has advantages and disadvantages. Limitations include restriction of individual files over 4GB size. A single file of more than 4GB size can’t be transferred to a FAT32 formatted USB drive. It lacks the permissions and other security features built into the more modern NTFS file system.
exFAT File System:
exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table) is the file system optimized for flash drives. It’s designed to be a lightweight file system as FAT32 but with certain advantages over NTFS.
Features: Like NTFS, exFAT has the very large file size and partition size limits. This means you can store files that are larger than 4 GB apiece on a flash drive or SD card if it’s formatted with exFAT. exFAT is a strict upgrade over FAT32 and should be the best choice for external drives where you want a lightweight file system without FAT32’s file size limits.
Compatibility: exFAT is also more compatible than NTFS. Works with all versions of Windows. While Mac OS X includes only read-only support for NTFS, Macs offer full read-write support for exFAT. exFAT drives can be accessed on Linux by installing the appropriate software.
Choosing exFAT file system while formatting USB drive:
- larger than 32 GB planning to use with the latest operating systems for Mac and Windows should be formatted in exFAT.
- choose when your file size is more than 4GB because the default option, FAT32, supports individual file sizes up to 4GB
It’s not support for older devices is one of the major drawbacks. And also, exFAT requires additional software to read on Linux distros.
Best one to choose — NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT?
- Choose exFAT — if the USB drive is used on Windows or Mac (Linux requires FUSE) and also if you are transferring files larger than 4GB.
- Choose NTFS — if the flash drive is used to install Windows software or transfer files larger than 4GB.
- Choose FAT32 — if the USB drive is smaller than 32GB and doesn’t require any security should be formatted in FAT32. Use it for ordinary works like transferring low-size files (lesser than 4GB).
If you know, some more features and limitations of these file systems tell us. We’d love to hear from you in the comments!


Bro how can I change it.i mean to say that how can I change raw to fat32.
superb one