AMD has introduced the Precision Boost Overdrive 2 (PBO2) for the Ryzen 5000 series processors.
With this feature, if you combine a Zen 3 CPU with a 500/400 motherboard, including Agesa v1.1.8.0, you will be able to explore the processors’ clock potential in a particularly fine-grained manner. Compared to the previous PBO, PBO2 will not be suitable for automatic overclocking of all CPU cores and will increase single-thread performance.
The first firmware updates should be available in December 2020. For the time being, PBO2 will be integrated with the UEFI. Next year support will also be implemented in the Windows tool from AMD called Ryzen Master.
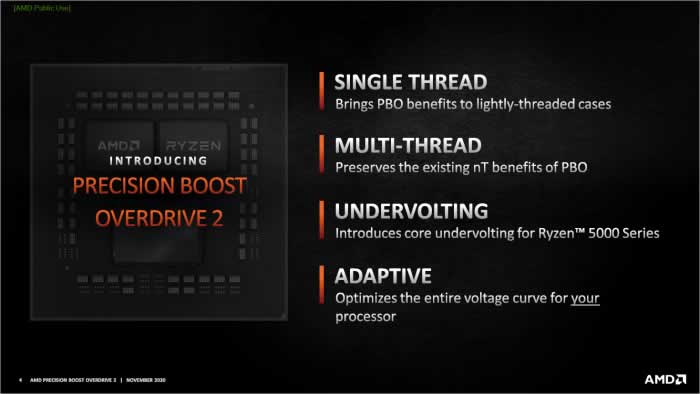
PBO2 uses a new tool — Curve Optimizer, with which the clock/voltage curve can be adjusted for each individual core.
So far, PBO has increased the clock rate depending on the PPT, EDC, and TDC parameters of the respective mainboard by up to +200 MHz per general voltage increase for all cores. With PBO2, on the other hand, there are up to 30 levels per core, each ranging from 3 mV to 5 mV — i.e. 0.09 volts to 0.15 volts up or down. The algorithm should behave intelligently and read out the internal sensors of the CPUs in a millisecond.

This means that individual, multiple, or all cores run adaptively with lower voltage and higher clock rates. With CPUs with many cores — such as the Ryzen 5950X (16 Cores) — the potential is better than with those with few, such as the Ryzen 5 5600X (6 Cores).
The best choice should be the Ryzen 5 5900X, as it has two CCDs and six instead of eight cores per CCD. AMD itself speaks of +3 percent (single thread) to +10 percent (multithread) additional performance through PBO2, measured with Cinebench R20 1T and Cinebench R20 nT.