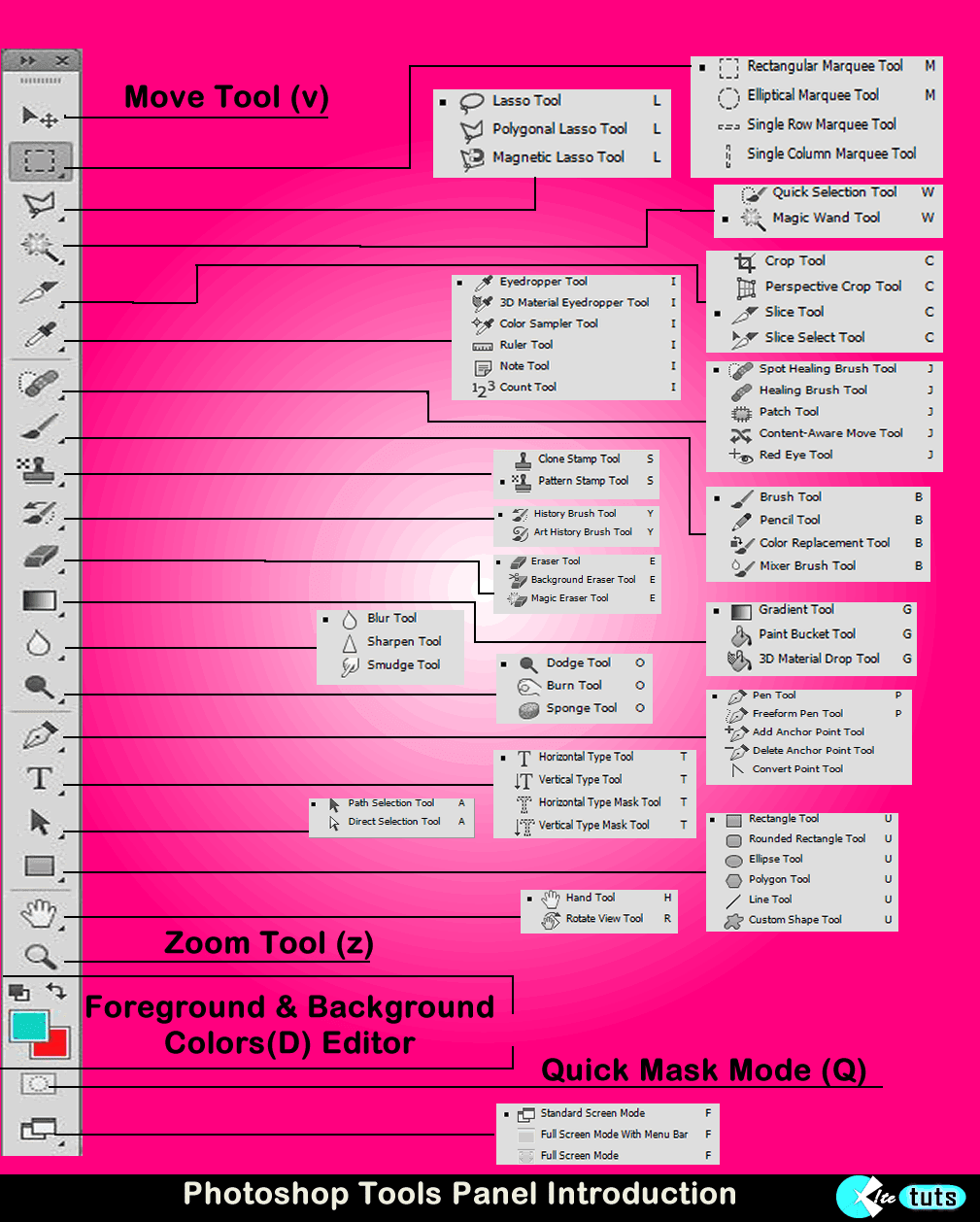
In this post we will discuss about the remaining sets of tools in photoshop.In last tutorial we ended our post with Brush Tool, Pencil Tool, Color Replacement Tool,Mixer Brush Tool.So now we are going to see 9th tool in photoshop:
►Clone Stamp Tool, Pattern Stamp Tool (S)
The Clone Stamp Tool has a lot of uses and if you’re doing photo manipulations then this a tool to be on good terms with. It is not complicated at all. To use it first Alt-click somewhere to set the sample point. Then start painting. You will notice that you will paint with the pixels underneath the sampled area. That’s all this tool does. It clones areas from one part of the image in other parts. It is very useful for creating new content based on an existing one and removing skin imperfections or undesired objects.
The Pattern Stamp Tool allows you to paint with desired patterns over an image. Never had a use for it!
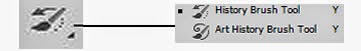
►History Brush Tool, Art History Brush Tool (Y)
The History Brush Tool is an interesting little thing that holds a lot of power. It allows you to paint on a new layer from a previous state of your image. Let’s say that you heavily modified a photo but you still want some of the original look in certain areas. To do this first select a previous state. Open Window > History and click on one of the little squares next to the name of the desired state. In the image below notice that I clicked on the little box next to the most upper state of the image – the original. Now if I create a new layer and paint with the history Brush Tool I can restore certain areas of my picture to their original state.
The Art History Brush Tool is a strange tool that allows you to paint from previous states of the images but in crazy, dynamically changing shapes. A quite useless little tool, if you ask me.
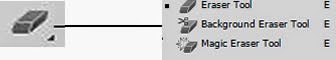
►Eraser Tool, Background Eraser Tool, Magic Eraser Tool (E)
The Eraser Tool allows you to delete (erase) pixels from a pixel layer (or a layer mask). It is as simple as that. You don’t like the way your new painted layer looks, you select the Eraser Tool and send pixels into oblivion. Alternatively, if you’re smart you could use a layer mask and nondestructively remove the undesired pixels. Maybe you noticed that I generously used the term nondestructive but I do this for good reason. When working on a document in Photoshop it’s very important to be able to go back and redo or modify some of your old actions. This offers you the power to infinitely tinker with settings and adjustments without losing any permanent data. That is why I recommend staying away from the Eraser Tool as much as possible and go for layer masks instead. A bit trickier to understand at first but they are totally worth the effort.
The Background Eraser Tool is like the Color Replacement Tool , but instead of replacing the color you erase it. It is a decent tool for getting rid of certain parts of the image but not precise enough. There are much better selection tools and techniques (like Channels and Color Range) that I do not use this tool very often.
The Magic Eraser Tool looks and acts a lot like the Magic Wand Tool but instead of selecting pixels it deletes them. Useful tool only if you are in a great hurry and do not care much about the results.
►Gradient Tool, Paint Bucket Tool (G)
First, let us cover the Paint Bucket Tool. It is a useless tool as far as I am concerned because I never used it. And I mean never ever. What does it do? Well, if you click with it on a picture it will fill the area with the foreground color. It has a Tolerance setting in the options panel which works the same way as the Tolerance setting for the Magic Wand Tool.
Now the Gradient Tool is a very useful tool and I find myself using it on a daily basis. It allows you to create a gradient from the background and foreground colors. The shortcut key is G. While you can achieve some artistic effects by dragging the gradient tool directly on a layer and then maybe use Fade (Ctrl + Shift + F) and an Opacity option it’s more likely that you will want to use it in layer masks.
►Blur Tool, Sharpen Tool, Smudge Tool
The Blur Tool and the Sharpen tool have some obvious purposes: they blur and respectively sharpen. They have 2 big disadvantages though. Firstly, they are pretty processor intensive, so if you like working fast or you have a slow machine you will have to wait. Secondly, using them means that you are not editing your document in a non-destructive way. If you want to go back to a previous look of your image then you will have to hit Ctrl + Z (Undo) like crazy. When it comes to sharpening and blurring I prefer to create composite layer from all the visible layers (Ctrl + Shift + Alt + E), apply a sharpen/blur filter on this layer, add a layer mask and paint it with black and white to show/hide my layer (in a layer mask black conceals and white reveals).
The Smudge Tool allows you to “smudge” pixels. It’s main use (at least for me) it’s to create hair. Let’s say I cut and copy in a document a wolf (or a human head) but I don’t select the hairs very well so it looks fake. Then I use the smudge tool at the edge of the fur to emulate hair.
►Dodge Tool ,Burn Tool , Sponge Tool (O)
Dodge Tool lightens and Burn Tool darkens while in the same time increasing contrast. In the Options Panel there are 2 setting you should be aware of: Exposure setting and Protect Tones checkbox. You will want to have the Protect Tones checkbox checked all the time unless you are aiming for very strong effects. The Exposure setting affects the power of the tool .I recommend using lower settings and gradually paint until you achieve the desired effect. A quick tip: If you are using the Dodge Tool hold Alt to temporarily switch to Burn Tool and vice versa.
The nondestructive alternative to these 2 tools is to create a new layer, fill it with 50% Gray color (Shift + F5), set the blend mode to Overlay and use Dodge and Burn or a black and white brush on the layer to achieve similar effects.
The Sponge Tool desaturates the image (absorbs color). For a more contrasty effect be sure to check the Vibrance checkbox in the Options Panel.
►Pen Tool, Freeform Pen Tool, Add Anchor Point Tool, Delete Anchor Point Tool, Convert Point Tool (P)
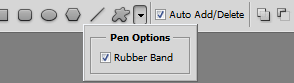
The Pen Tool may be familiar to you if you have worked with Adobe Illustrator. This tool allows you to create vector shapes and the additional tools in the category allow you to modify and tweak that shape. I don’t do much vector work but instead I use this tool heavily for my selections. Basically I trace with the pen tool the object I want selected and then I simply transform path to selection (Ctrl + Enter). This allows me to do very accurate selections, it works especially well when the object I want to select has a color similar to the background, and the usual selection techniques will not work. So go ahead, give it a spin and create some paths. Make sure to check Rubber Band in the Options Panel as it allows you to preview the paths you are going to create.
►Horizontal Type Tool, Vertical Type Tool, Horizontal Type Mask Tool, Vertical Type Mask Tool (T)
Horizontal and Vertical Type tools allow you to add text to your images. Simply click anywhere in your document with one of these two tools and start typing. You can change the font, size and other settings in the Options Panel. When you are done typing simply press Ctrl + Enter to close the paragraph and stop typing. If you click and drag with one of these two tools you will create a box which will allow you to type only inside that box.
If you want to type on a path for a special effect simply create a path with the Pen Tool and with Vertical or Horizontal Type Tool click somewhere on the path (you will notice that the icon will change).
Horizontal and Vertical Type Mask tools allow you to create a selection from type. That is if you type something with one of these tools and press Ctrl + Enter you will have a selection of your typed text. I don’t use these tools at all because I can get a selection from a type layer much easier: I simply Ctrl-click on the layer and voila, a selection of the visible pixels of that layer.
►Path Selection Tool, Direct Selection Tool (A)
These tools are designed to manipulate and select paths. If you click with the Path Selection Tool on a path you will select the entire path and if you click with the Direct Selection Tool on a path you will select only a point or a handle bar.
►Rectangle Tool, Rounded Rectangle Tool, Ellipse Tool, Polygon Tool, Line Tool, Custom Shape Tool (U)
These tools allow us to create different shapes. There are three options in the Options Panel which are very important. If you select the first option you will create Shape Layers (that is basically a Solid Color Adjustment layer with a Vector Mask), the second option allows you to create simple Paths and the third option allows you to create pixel shapes.
►Hand Tool (H) and Rotate View Tool (R)
If you are zoomed into a document the Hand Tool allows you to drag the document. Simply click and drag and you will see what I am talking about. You can temporarily access the Hand Tool from almost any other tool by simply holding the Space button.
►Zoom Tool
The Zoom Tool allows you to zoom into a document. Drag to the left to zoom out or drag to the right to zoom in. Click to zoom in, Alt-click to zoom out. You can temporarily access the Zoom Tool from almost any tool by holing Alt + Space. Note that certain features of the Zoom Tool and the Hand Tool won’t work if you don’t have Enable OpenGL Drawing checked in the Edit > Preferences – Performance tab.
There are some additional buttons on the Toolbar Panel which are not Tools.
Default Foreground And Background Color (Shortcut D) allows you to set black as foreground color and white as background.
Switch Foreground and Background Color (Shortcut X) allows you to switch between foreground and background colors.
Set Foreground and Set Background Color. If you click on one of these icons the Color Picker window will pop up allowing you to select a color. A nice feature of Photoshop CS5 is that when you have the Brush Tool selected you can temporarily access a simplified version of the Color Picker window (also called HUD Color Picker) by holding Shift + Alt and Right-clicking. You can change some options for the Color Picker appearance by going to Edit > Preferences > General.
Quick Mask (or Edit In Quick Mask Mode) (Shortcut Q) allows you to quickly select parts of your document.
And finally the last button in photoshop interface Screen Mode Button.As name implies its used to adjust screen and its shortcut is F.
♣ Conclusion
This is where I finish my introduction to the Photoshop Toolbar. I hope you have become more familiar with the different Photoshop Tools and learned some useful stuff.