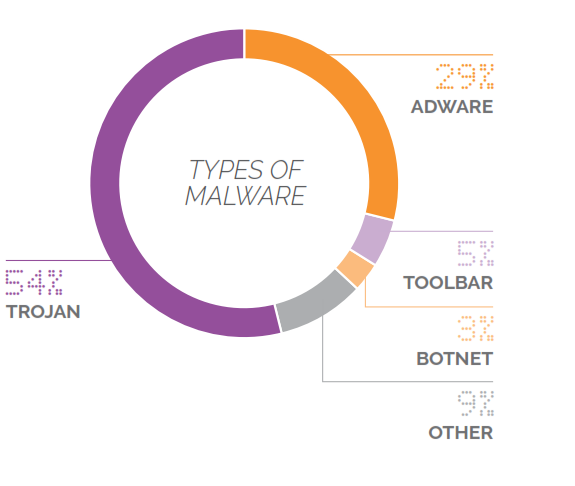
Technology giant Google hopes to bring its Project Loon to India, which will offer affordable internet access to millions, soon even as the government holds the view that the project will interfere with cellular transmissions of mobile operators in the country.
Speaking at the Google for India event, the company’s CEO Sundar Pichai said: “Project Loon will launch balloons in the sky to help reach out to rural areas.”
What is Project Loon ?
Also Read : Now Google Lets You To Use Apps Without Installing Them On Your Phone
The service will provide high-speed Internet for the first hour before downgrading to a lower speed post that. The service however will remain free throughout the access period. When asked about the expected speed, Gulzar Azad, Google’s head of access programs – India, refused to divulge details on the speed but said that users will be able to watch HD-quality videos during the first hour, adding that the speed will be faster than what the average speeds in India are.
Google also said that it is expanding its program with Tata Trusts to connect women in rural India through a fleet of Internet bikes. The program has reached 1,000 villages so far and aims at a target of 3 lakh villages nationwide within three years.
Also Read : Google Says its Quantum Computer is More Than 100 Million Times Faster Than a Conventional PC
Elaborating the same, Google Vice President (Access Strategy and Emerging Markets) Marian Croak said the company is “passionate” about building and deploying new Internet infrastructure around the world.
“One of the technologies that we have in our portfolio is Project Loon. It’s a project that we are working on with local telcos all across the world. “And we are testing these high altitude balloons which literally act as almost like floating cell towers… To connect people in hard to reach regions that are scarcely populated and we are working to hopefully bring Project Loon to India in rural communities that have very few people connected to the Internet,” — she said.
The statement assumes importance as Communications and IT Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad had recently told Parliament that Google’s Project Loon will interfere with cellular transmissions of mobile operators in India.
“The proposed frequency band to be used in the Loon Project of Google is being used for cellular operations in India and it will lead to interference with cellular transmissions,” — Prasad had said in a written reply to the Rajya Sabha on December 11.
Also Read : Google Announced A New Project To Provide High-Speed Public Wi-Fi In 400 Train Stations Across India
Croak said the company is working across the world with local carriers, operators and suppliers and does not carry out the project on its own.
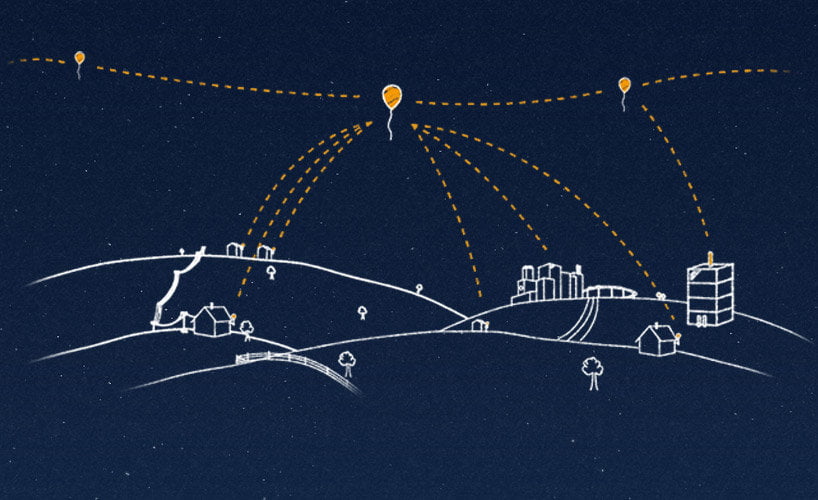
Google, under its Project Loon, is using big balloons floating at a height of 20 kilometers above earth surface for transmission of Internet services. It has already tested this technology in New Zealand, California (the US) and Brazil. As per Google, each balloon can provide connectivity to a ground area about 40 kms in diameter using a wireless communications technology called LTE or 4G.
To use LTE or 4G, Project Loon partners with telecom companies to share cellular spectrum so that people will be able to access the Internet everywhere directly from their phones and other LTE-enabled devices. Google uses solar panel and wind to power electronic equipment in the balloon throughout the day.
Also Read : Top Android Apps that Drain Battery and Use Up all your Data and Storage
So what do you think Google’s Project Loon service, Does it will help us to stay connected to our loved ones from any part of India? We’d love to hear from you in the comments!