Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder, in collaboration with the University of California, Berkeley and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), have developed a groundbreaking light-based microprocessor chip to create more powerful computers and ultrafast communications. Since this microprocessor chip uses light, rather than electricity, to transfer data at rapid speeds while consuming minute amounts of energy.
The technology involved in creating light-based microprocessor, called silicon photonics, is an active area of research at chipmakers like Intel and IBM. The new light-based microprocessor measures just 3 millimeters by 6 millimeters and utilises multiple wavelengths of light, simultaneously sending data through a single fibre. And the new chip has the potential of transmitting data at nearly 300Gbps per square millimetre, which is close to 50 times faster than conventional electronic wires.
Also Read : Power Paper – A Paper to Store Electricity Coming Soon
Why Light-Based Microprocessor Chip
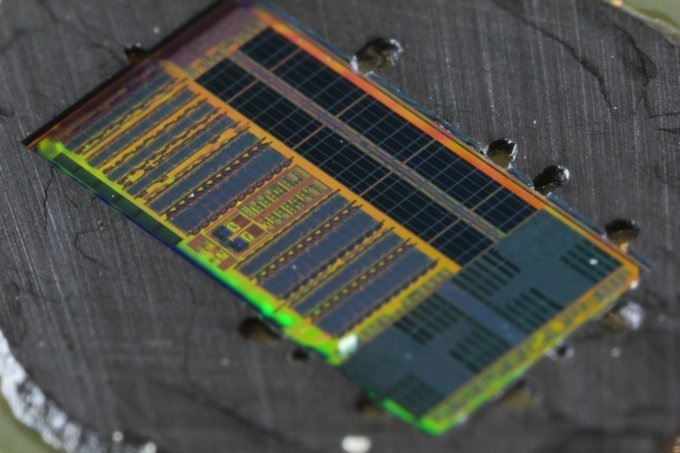
Data transport across short electrical wires is limited by both bandwidth and power density, which creates a performance bottleneck for semiconductor microchips in modern computer systems—from mobile phones to large-scale data centres. Since fibre optics offer larger bandwidth that could facilitate higher rate of communications over greater distances. Fibre optics also utilises less energy. The prototype researchers used had fibre optic links instead of conventional electric wires, also demonstrating that optical chips can be made without any alteration to existing semiconductor manufacturing processes, which has been a challenge thus far.
“One advantage of light based communication is that multiple parallel data streams encoded on different colors of light can be sent over one and the same medium – in this case, an optical wire waveguide on a chip, or an off-chip optical fiber of the same kind that as those that form the Internet backbone,” — said Popović, whose CU-Boulder-based team developed the photonic device technology in collaboration with a team led by Rajeev Ram, a professor of electrical engineering at MIT.
“Another advantage is that the infrared light that we use – and that also TV remotes use – has a physical wavelength shorter than 1 micron, about one hundredth of the thickness of a human hair,” — said Popović. “This enables very dense packing of light communication ports on a chip, enabling huge total bandwidth.”
Also Read : Li-Fi Is Here, 100 Times Faster Than Wi-Fi
Future of Light-Based Microprocessor Chip
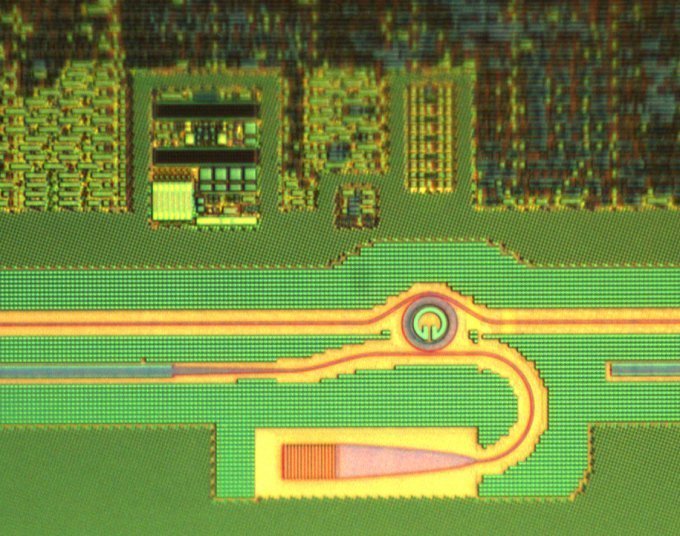
The new light-based microprocessor chip bridges the gap between current high-speed electronics manufacturing and the needs of next-generation computing for chips with large-scale integrated light circuits.
Also Read : Nanoparticle Quantum Dot Will Charge Your Phone In 30 Seconds
If they succeed in bringing their prototype out of the research lab, consumers will eventually benefit. For data centers, where messages shuttle among thousands of servers, silicon photonics could speed up services like Google search or Facebook image recognition or let those companies introduce performance-intensive features not economical today. For personal computers and smartphones, silicon photonics could uncork performance bottlenecks without hampering battery life.
“Light based integrated circuits could lead to radical changes in computing and network chip architecture in applications ranging from smartphones to supercomputers to large data centers, something computer architects have already begun work on in anticipation of the arrival of this technology,” — said Miloš Popović, an assistant professor in CU-Boulder’s Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering and a co-corresponding author of the study.
So when can we expect it? The researchers are expecting that data-centers will be the first to utilise the chips, and they will eventually find their way into the mobile and PC market. They also expect the test versions of these chips to be ready by early 2017. The team has published a paper in the journal Nature.
Also Read : A Smart Glove That Translates Sign Language Into Text And Speech
What do you think about this new light-based microprocessor chip. Do they opens new door to more advanced technology? We’d love to hear from you in the comments!