Front-end development, also known as client-side development, is the process of creating the User Interface (UI) of a website or online application, which specifies how each component of a website will look and work. The UI is made up of the visual parts of the application as well as user interactions. All of the features you see on a website are created by the front-end, including the many button kinds and other UI components, media, messages, forms, animations, and so on.
A software engineer that specializes in front-end development is known as a front-end developer. They are also responsible for maintaining a balance between design and functionality, speed, and scalability in addition to designing the user interface. They also guarantee that the website loads properly across all browsers (cross-browser), all platforms (cross-platform), and all devices (cross-device), including mobile phones, tablets, and computer screens.
The tools and techniques needed to build a website’s front end are always changing and these tools can be learned by enrolling in web development courses. The profusion of various front-end tools and frameworks can often befuddle newcomers who are trying to enter the front end because they are unsure of what they need to study. If you want to work as a front-end developer but aren’t sure where to start, here is the place for you. This article covers the programming languages, frameworks, tools, and technologies you should learn. We’ll talk about the Front End Developer Roadmap.
The field of frontend development is always changing, therefore success depends on remaining current with the newest trends and technology. This comprehensive book will give you a road map for navigating the frontend development industry, supported with pertinent data that emphasize the significance of each stage if you’re aiming to become one.
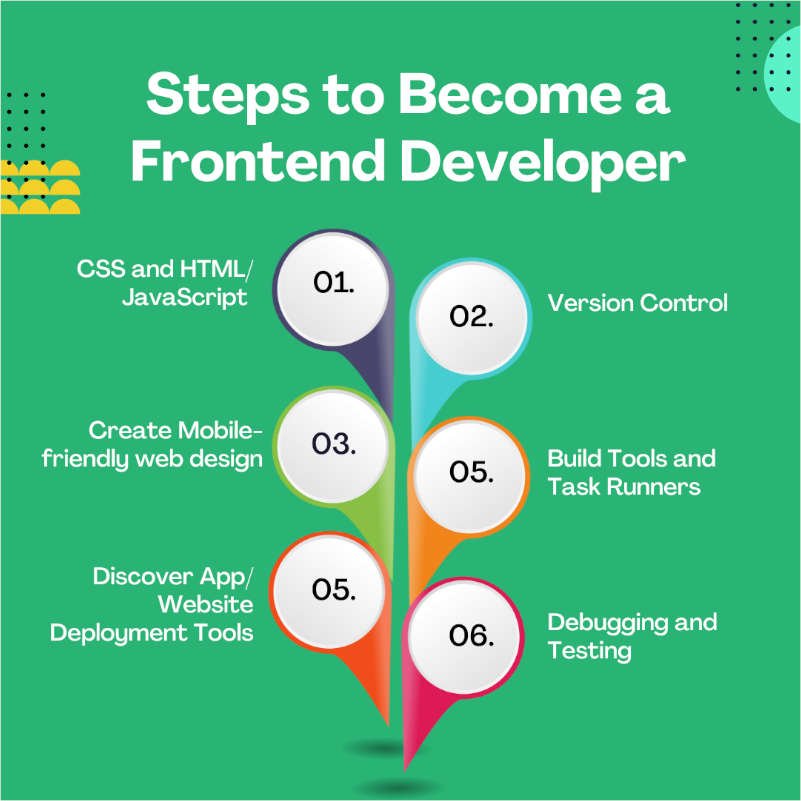
Roadmap for Front-End Developers: Steps to Become a Front-End Developer
Let’s look at the frontend roadmap. To reduce your learning curve, we advise taking an online front end web developer course. Geekster has the ideal learning path that is specifically designed for you, whether you are a total novice or an experienced programmer wishing to advance your skills. Everything you need to know to master the craft of web development is covered in our extensive curriculum, from fundamentals of HTML and CSS to sophisticated JavaScript frameworks and beyond.
Geekster is unique because we value experiential learning. Forget about theoretical topics that leave you perplexed and tedious lectures. At Geekster, we favor hands-on learning. Prepare to put your hands in your pockets and start challenging code tasks that mirror real-world events. Create beautiful websites, engaging web apps, and responsive designs to elevate your portfolio!
1. CSS and HTML
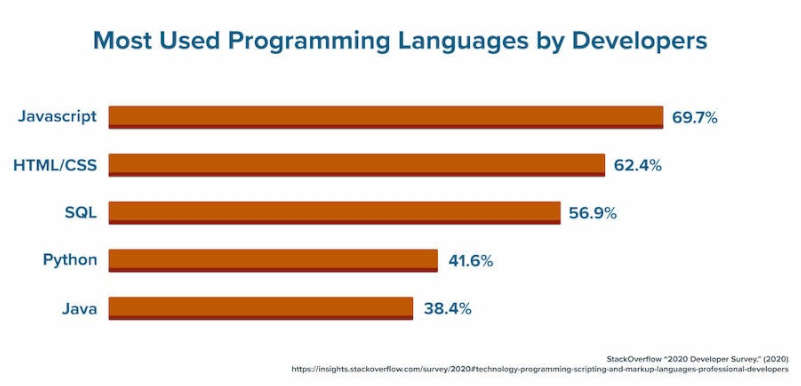
HTML and CSS are among the most widely used technologies, with 63.5% of developers utilizing them, according to the 2020 Stack Overflow Developer Survey. For developing well-structured and aesthetically pleasing web pages, proficiency in HTML and CSS is a requirement.
2. JavaScript
The foundation of web interaction is JavaScript. Your frontend development skills can be greatly improved by becoming familiar with the principles of JavaScript and cutting-edge frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js. Since these frameworks are built on top of JavaScript, all of the framework’s functionality can also be implemented using normal JavaScript. But these frameworks offer enhanced capabilities without necessitating the writing of new code. This is the justification for why front end developers usually choose frameworks to straightforward JavaScript.
Some of the well-known JavaScript frameworks for front-end development include Angular, React, Vue.js, and Meteor.
3. Version Control
For collaborative work, version control tools like Git are essential. 87.5% of developers use Git, according to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2020. The ability to manage code effectively, collaborate, and integrate with sites like GitHub, which houses millions of open-source projects, is made possible by learning version control. Instead of having to manually undo changes, this software lets you manage and track source code changes and go back in time to a previous version. It increases the development experience and speed since you spend less time managing the code, there are fewer chances of code conflicts, and it makes it easier to recover your code if you need to return to an earlier version.
One of the most well-liked and commonly used version control systems is called Git.
4. Mobile-friendly web design
For seamless user experience across devices, responsive web design is essential. In the first quarter of 2021, mobile devices accounted for 54.8% of all internet traffic worldwide, according to a Statista analysis. With the growing popularity of mobile devices, responsive design has become an essential component of frontend development.
To provide the best user experience, websites must adapt to different screen sizes and orientations. Think about elements like color contrast, keyboard navigation, using alt text for photos properly, and semantic HTML. You can make sure that all users can access and utilize your websites efficiently by putting accessibility best practices into practice.
Make sure your websites are accessible to persons with disabilities by understanding the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
5. Web performance optimization
User satisfaction and conversion rates are directly impacted by website performance. According to Google’s research, the likelihood of a bounce increases by 90% as page load time rises from one to five seconds.
Delivering quick and effective experiences requires optimizing website performance through file compression, caching, and code minification. Learn how to reduce website page load time through file sizes and limit network requests by using techniques like minification, compression, caching, and lazy loading.
Check out WebPageTest or Lighthouse to examine and improve the performance of your website. Delivering a quick and effective user experience ought to come first.
6. Build Tools and Task Runners:
Build tools and task runners increase productivity by streamlining development operations. With 58.9% of developers using it, Webpack is the most widely used build tool, according to the State of JavaScript 2020 poll.
Your capacity to handle dependencies, bundle assets, and optimize code can be improved by learning how to configure and use build tools.
Chrome DevTools, Firefox Developer Tools, and Safari Web Inspector are powerful tools for frontend developers.
7. Discover App/ Website Deployment Tools
Once your website is completed, you must launch it so that anyone with access to the internet may view and utilize it. You must understand the fundamentals of hosting tools in order to deploy a website. Here is a typical App development Roadmap followed by big MNC’s.
Tools like Github Pages, Heroku, Firebase, Netlify, Vercel, and others are available. Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure also offer hosting services.
8. Debugging and Testing
Code quality assurance depends on efficient testing and debugging procedures. 87.7% of JavaScript developers write tests, per the State of JavaScript 2020 survey.
You may write automated tests and find potential flaws early in the development process by learning testing frameworks like Jest or Cypress, which will result in more robust and reliable code.
9. Create a Portfolio
Congratulations! You’ve become a front end developer by mastering the aforementioned abilities. Next, what? You could, however, submit applications for positions in front end development. The difficulty is that there are many applicants for a limited number of positions in the highly competitive industry of front end development. Building your portfolio is a smart move if you want to distinguish out from the competition.
An online portfolio is a place where you may share details about yourself,
web development final year projects, your background, your experiences, your talents, a sample of or a link to one of your previous work, references, etc. You’ll be able to demonstrate your abilities and improve your reputation and exposure in the field. You can host your portfolio online so that prospective employers and hiring managers can view your prior work.
10. Continuous Learning: Remaining Current and Active
The world of frontend development is continually changing, with the emergence of new technologies and best practices. Follow notable developers, sign up for newsletters, and participate in online communities to stay informed. Attend conferences, workshops, and meetups to gain knowledge from business leaders and connect with other developers. To stay ahead in the field, always broaden your knowledge and stay current with the newest web development frameworks and trends.
Conclusion
The path to become a frontend developer is one that is rewarding and fascinating. You will have a road map to follow as you proceed through the crucial knowledge, resources, and ideas needed for front-end development by following this comprehensive tutorial. Build practical tasks, practice frequently, and value lifelong learning. Keep an open mind, be adaptable, and enjoy the journey to become a proficient frontend developer because the field is constantly changing.
Remember that this road map is only meant to be a learning tool and not a set of rigid rules. It’s crucial to keep up with changes in web tools and technology and to upgrade your knowledge. After conducting your own research, you may always select the study path that best suits your schedule, budget, and skill level.