Microsoft releases security updates for Windows at regular intervals to fix the latest bugs found on your system and prevent hackers and viruses from taking over your system. Due to the complexity of Windows and, above all, since Windows is installed on computers with different types of hardware, some updates could be defective, causing new instability problems or even causing the operating system to freeze (BSOD or blue screen error).
If we have encountered this unpleasant problem, we can fix it by applying one of the methods described below to uninstall the Windows updates that cause errors or malfunctions.
This guide will be based on the latest operating system supported by Microsoft, namely Windows 11. Still, many of the proposed changes or solutions can be applied to Windows 10, Windows 8.1 and Windows 7 too.
Uninstall Windows updates from Settings
In Windows 10, you can view the update history by opening the Settings app from the Start menu, heading to the Update and Security menu, selecting Windows Update, and then clicking on the View update history option.
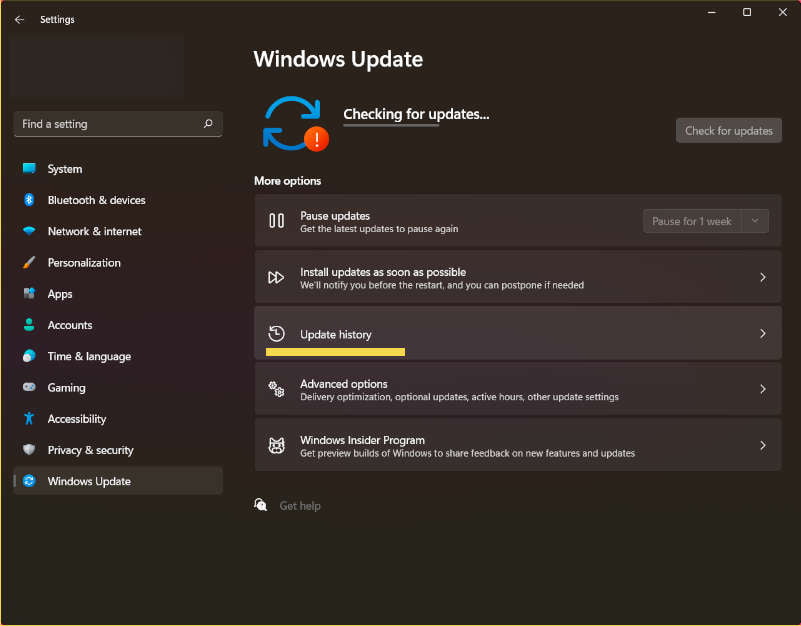
In Windows 11, it’s the same thing, only that the update history is located in Settings > Windows Update > Update History.
Once this window is open, scroll down and click on Uninstall updates to open the specific window where you can uninstall the most recent updates (those we suspect have caused the problem with Windows).
If the update has changed the current version of Windows 10 or Windows 11 installed (i.e. we have installed a major update), we can uninstall it and go back to the previous version to continue using the computer without problems; however, avoid skipping too many major updates, which might result in other security issues.
Uninstall Windows updates from Control Panel
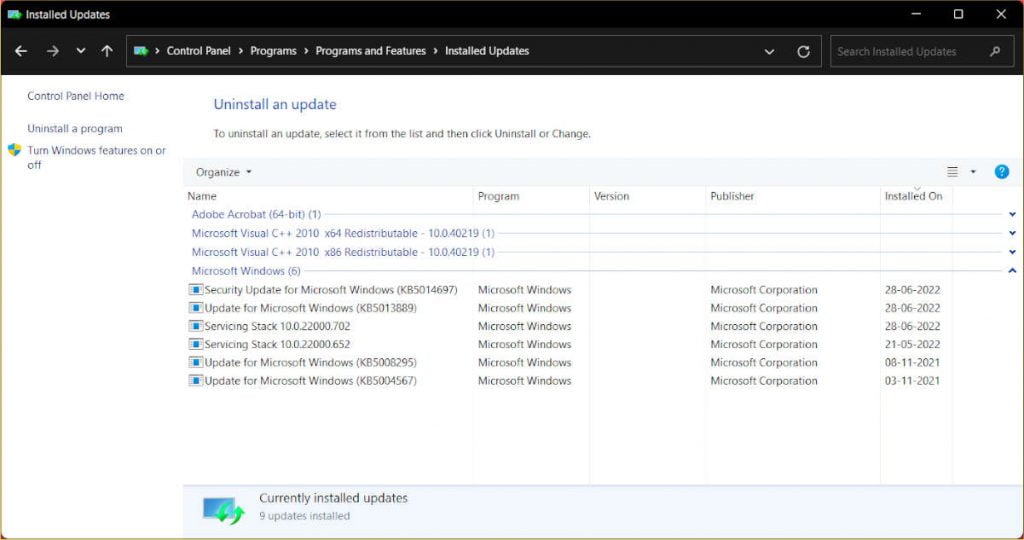
Open the Control Panel (we can always look for it from the Start menu) and click on Uninstall a Program to delete patches and updates the old-fashioned manner on any version of Windows (under the Programs section). From the uninstall programs window, click on View installed updates from the options on the left and look for the updates to remove.
For convenience, we can use the search box and write the abbreviations (for example, KB2982791 and KB2976897 ) or search for them manually by sorting the updates by installation date (click on the header of the column Installed on ). Having identified the update to be removed, right-click on it and remove it. Windows may ask you to restart your PC to complete the operation.
Uninstall Windows updates from the Command Prompt
For geek and expert users, it is also possible to uninstall updates from the command prompt using the WUSA(Windows Update sandbox) tool. In this situation, you must know the version of the update (KBXXXXXXXX) that you wish to uninstall and input it by hand to avoid errors.
To do so, press the Windows key, enter cmd.exe, right-click Command Prompt, and select Run as administrator to open a command prompt with administrative rights. Once the black Prompt window is open, we can remove an update by writing the following command:
wusa /uninstall /kb:2982791
Obviously, the KB string must be replaced with that of the update that caused problems or that we want to remove immediately.
Remove Windows updates on a locked PC
Suppose the computer does not start or is completely locked out after performing a new update. In that case, we can restore to a known working version of the system by starting the recovery console and pressing Troubleshoot, then on Advanced options and finally on System recovery.
We select the system to restore and wait: with a little luck, we will go back in time before installing the update.
Suppose we cannot start Windows 8.1 or Windows 7. In that case, we can repeatedly press the F8 key when starting the computer and remove the updates using the latest restore point, selecting the Last known good configuration.
Fortunately, errors in updates are not frequent. Still, they can always happen, and since we work on computers, it is worth knowing all the methods available to remove the problematic updates.